Conjugate-Cam FB
See: Add Conjugate Cam FB.
What is a Conjugate Cam?
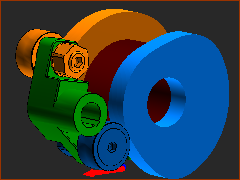 A Conjugate Cam pair |
Conjugate Cams (typically two Cams) rotate on one shaft, with each cam in contact with a Follower-Roller, and in which the Follower-Rollers are rigidly attached to one Follower-Part. For example: In the image, the blue and orange Cams rotate together on one shaft (the shaft is hollow!). The blue Cam-Profile is in continuous contact with the blue Follower-Roller, and the orange Cam-Profile is in continuous contact with the orange Follower-Roller. The two Follower-Rollers are rigidly attached to the green Follower-Part. |
Why use a Conjugate Cam FB?
Typically, one Cam is the Power-Source for the Follower-Part and kinematic-chain. However, if Conjugate Cams are the Power-Source, you must add, edit, and configure a Conjugate Cam FB and then select the Conjugate-Cam FB as the Power-Source. Only then should you do the force and stress analysis. Groove Cams are also conjugate-cams. However, you cannot use the Inner and Outer flanks of one 2D-Cam as the Conjugate-Cams. In a machine, a Groove Cam may use one or two Follower-Rollers. To model a Groove-Cam and also complete its force and stress analysis, you need to add two co-axial Follower-Rollers and two Cams. You must select the Inner Cam as one Cam-Profile, and the Outer Cam as the Conjugate Cam-Profile. Then add, edit and select the Inner and Outer Cams in the Cam-Conjugate dialog, and select the Cam-Conjugate FB as the Power-Source. |
2D-Cam Work-flow
Action |
Help Topic |
|---|---|
Before you start this work-flow: add a kinematic-chain for the Cam-Part and a kinematic-chain for the Follower-Part; add mass-properties to the Parts; develop the motion design. The two kinematic-chains must be kinematically-defined. |
|
1.Add a 2D-Cam; or if Conjugate Cams then 2 × Follower-Rollers and 2 × 2D-Cams; or if a Groove-Cam then two concentric (co-axial) Follower-Rollers with one for the Inner-flank only, and the one for the Outer-flank only. |
see Add 2D-Cam |
If the new 2D-Cam is one of two Conjugate-Cams, or it is one flank of a Groove-Cam, then: |
|
i.Add a Conjugate-Cam FB ii.Open the Conjugate-Cam dialog and select the one flank each from two 2D-Cams |
|
2.In the Kinematics-Tree, select the 2D-Cam or a Conjugate-Cam FB as the Power Source for the kinematic-chain that includes the Follower-Part |
|
3.Edit the 2D-Cam: to open the 2D-Cam dialog: review Display, Properties, Roller-Life, Cam-Life tabs |
see 2D-Cam dialog |
4.Add a Cam-Data FB |
see Add Cam-Data FB |
5.Edit the Cam-Data FB to link it to a 2D-Cam - close the dialog |
see Cam-Data dialog |
6.Connect wires from the output-connectors of the Cam-Data FB to a Graph FB |
|
7.Open the Graph FB to analyze the 2D-Cam: Contact-Force, Maximum Shear-Stress, Radius-of-Curvature, Pressure-Angle, Sliding-Velocity. |
|
8.Edit the Cam-Data FB again to calculate the Cam's Coordinates |
|
How to open a Conjugate Cam dialog
|
To open the Conjugate-Cam dialog:
|
The Conjugate-Cam dialog is now open.
Conjugate-Cam dialog
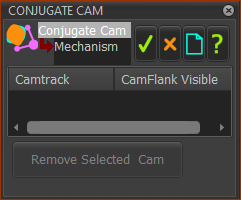 Conjugate-Cam dialog |
||
In the graphics-area or Assembly-Tree:
|
||
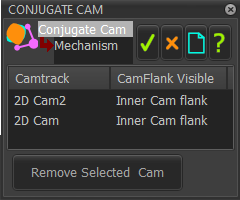 The two 2D-Cams are in one kinematic-chain and must be capable of being the Power-Source for one other kinematic-chain. Each 2D-Cam drives the Inner-Cam-Flank OR the Outer Cam-Flank.
Note 1 : If the 2D-Cams you select do not drive the same Follower-Part, you get this message in the Feedback Area. Message 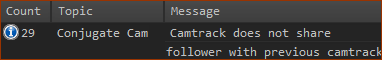 To do Force Analysis of the Conjugate Cams, you must select the Conjugate-Cam FB in the Configure Power Source dialog. To remove a 2D-Cam
|
Select Conjugate Cam in the Configure Power Source dialog
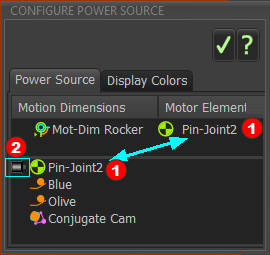 DEFAULT: Configure Power Source dialog |
|
Configure the Power Source
Now you can do Contact-Force Analysis for the Conjugate-Cams. |
|
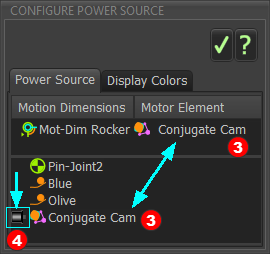 Conjugate-Cam as the Power-Source |
