Quadratic Cam-Law, Motion-Law
Motion Description
Motion-ValuesYou CAN control the:
You CANNOT control the:
Segment Parameters
Segment-Range
|
|||||
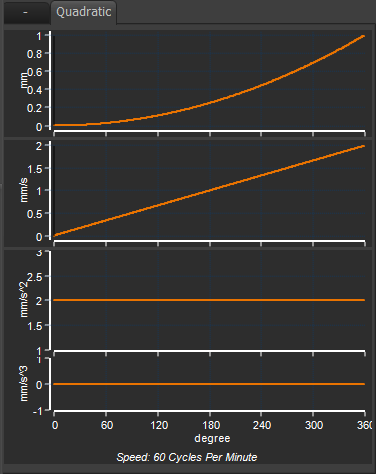 Quadratic Motion-Law |
|||||
In the image above of 1 Quadratic segment, the motion-values are: •Start Position = 0mm •End Position = 1mm •Start Velocity = 0mm/s Applications
|